Safe Junction
Safe Junction changes the perspective of bridges by positioning itself on a higher level, aiming to provide a universal cross-chain experience by using multiple oracles for compounded security and being faster than others thanks to its Fast Lane feature.
Project Description
Our protocol is designed to provide a superior cross-chain asset bridging experience, something we call the "meeting point" of bridges, the Safe Junction.
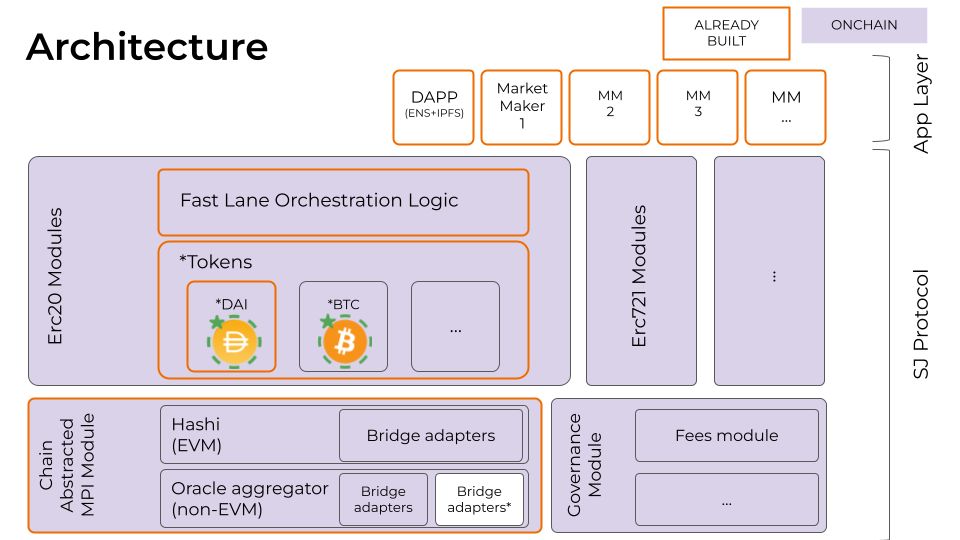
By using several bridges as oracles, Safe Junction achieves cross-chain asset transfer validations in a redundant, universal and safer way. It is designed to be chain agnostic and simple to audit. Yet, it achieves speed, thanks to a built-in optional feature called the Fast Lane.
Today the bridging ecosystem suffers from excessive fragmentation. Safe Junction powers *Tokens (“Star Tokens”) to tackle this very problem. These tokens inherit the properties described above to provide a superior cross-chain experience.
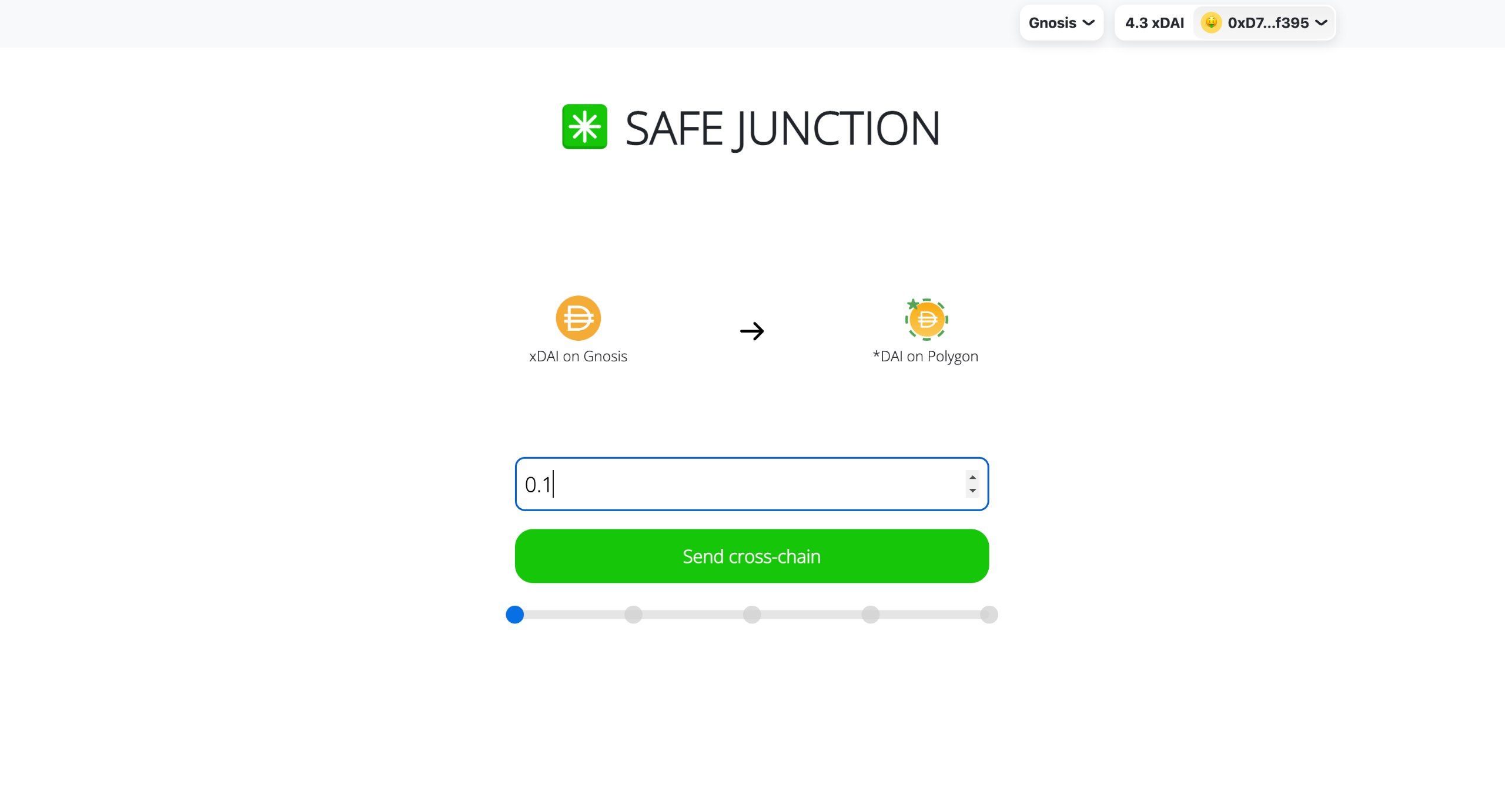
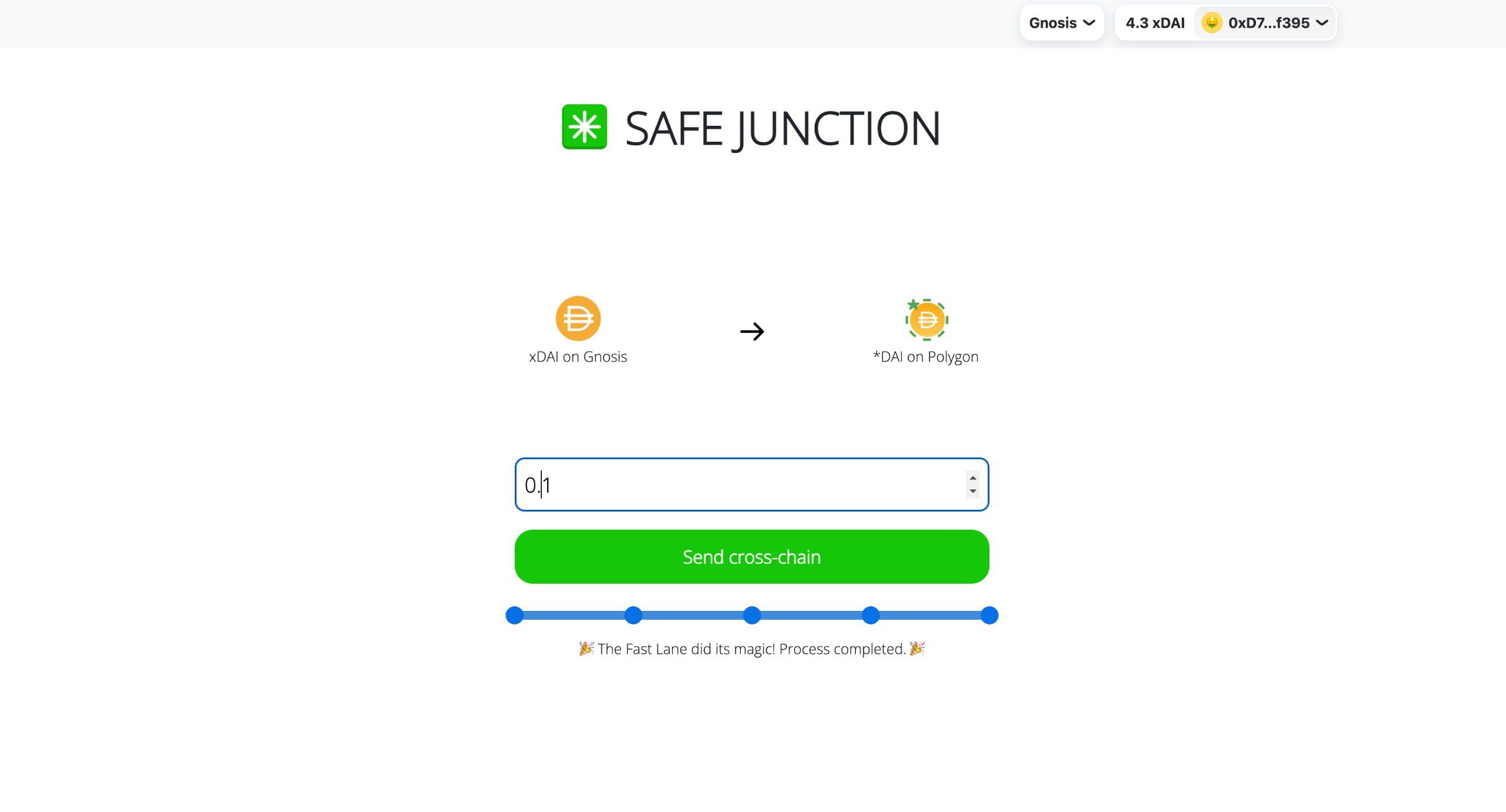
In the worst case, the system's speed is equivalent to that of the slowest oracle in the network. However, when the Fast Lane functionality gets used, it overcomes this drawback and enables much higher speed: market makers can process cross-chain transfers in advance, providing their liquidity in response to a user request, and then securely reclaim the liquidity (plus a service fee) once all oracles have processed the cross-chain request at their standard speed.
To make the protocol even more decentralized and inclusive for all stakeholders, a share of the protocol fees will be distributed to the partners (oracles) according to their contribution.
It is important to understand how Safe Junction differs from existing cross-chain solutions (bridges, aggregators, etc.) in terms of security (which is additive), speed (via Fast Lane MM intervention) and compatibility (as it aims to be 100% agnostic, and not just EVM compatible).
While the protocol aims to be fundamentally blockchain agnostic, the specific implementation for ETHGlobal Lisbon 2023 has been designed for EVM blockchains, and when used in this context it makes use of the Hashi EVM Hash Oracle aggregator.
How it's Made
The project is made of several components, all available on GitHub and whose architecture is explained in detail on the slides of the demo. A short description of the modules (what they do, how they are made) follows:
SAFE-JUNCTION-CORE: the core Safe Junction protocol smart contracts for EVM. They glue together the underlying oracle aggregator logic (i.e. Hashi for EVM chains) with core features of SJ such as Fastlane and the *Tokens contracts.
FASTLANE: it includes on-chain and off-chain logic to achieve orchestration of the Fast Lane feature. This enables market makers to speed up the processing of SJ transfers without taking risks (as they know after finality the tx will surely happen), in order to earn some fees.
HASHI-RELAYER: a simple component to reveal on the destination chain the message committed to on the originating chain.
DAPP: react powered frontend, it lives completely client-side and gets delivered to the user via ENS+IPFS entirely
DUMMY-ORACLE: to speed up tests during the hackathon, a dummy oracle adapter and off-chain agent that acts as an oracle
These components power the prototype instance that we have deployed to bridge xDAI from Gnosis Chain to Polygon. We are currently running 1 relayer, 1 market maker for the Fast Lane and 1 dummy oracle. Anyone can run any of these (clearly beside the dummy oracle, which is meant to be replaced in production by the existing oracle adapters for Hashi, so with real oracles) as they don’t require any permissioning.