Poseidon Swap
Swap your tokens cross-chain at the best rate by avoiding high slippage and price impact
Project Description
Our protocol has different use cases. The main one today is to be able to swap any token on whichever chain you want. This can be a huge advantage for blockchain users that have huge amounts of tokens on a chain with low liquidity pools.
We are able to make trades more efficient, faster and cheaper as the congestion issues persist on many chains. We could think that users might be able to swap on a different chain with Poseidon Swap when the fees on the source chain are too expensive.
Finally, with this protocol, we would be able to call functions on contracts that are on other blockchains, as long as the CCIP messaging service allows it. Appart from the ability to swap on the destination chain, which is the main focus of Poseidon Swap, this would create a new landscape for interoperability across blockchains, such as calls and messages of Gelato automation instructions.
How it's Made
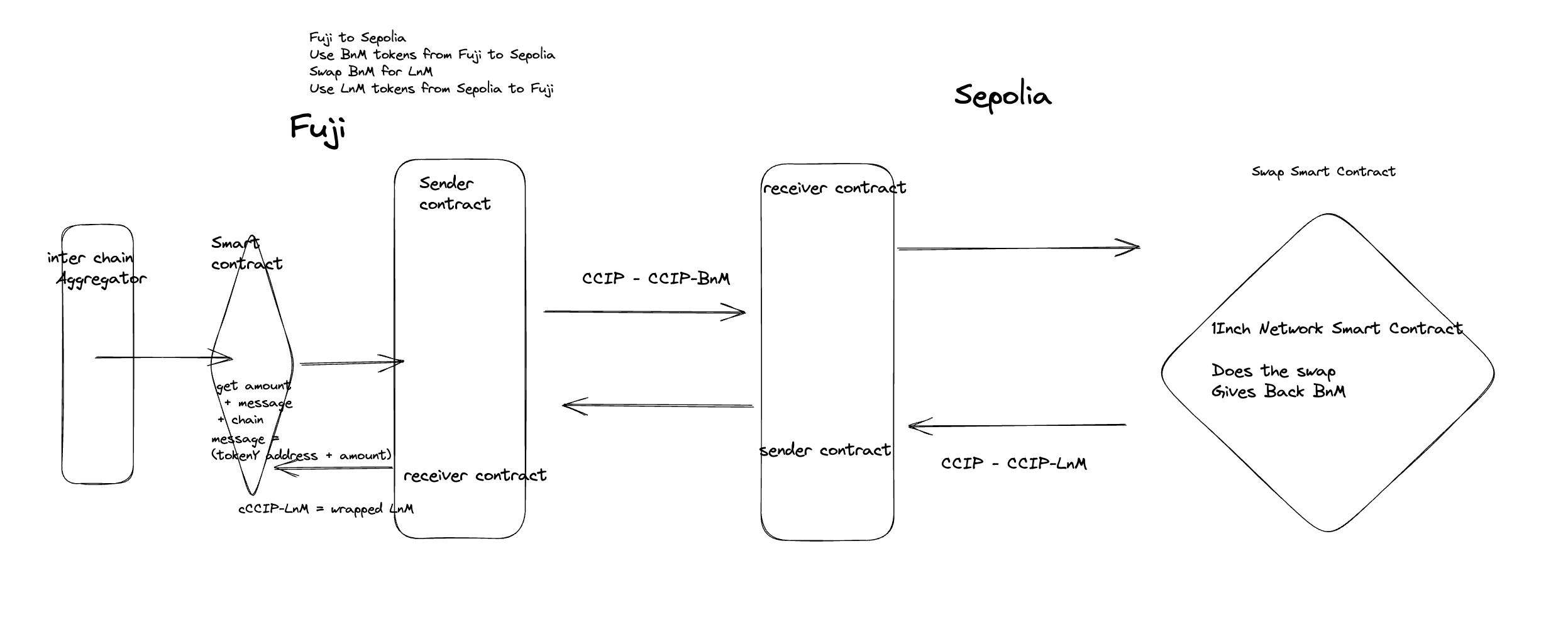
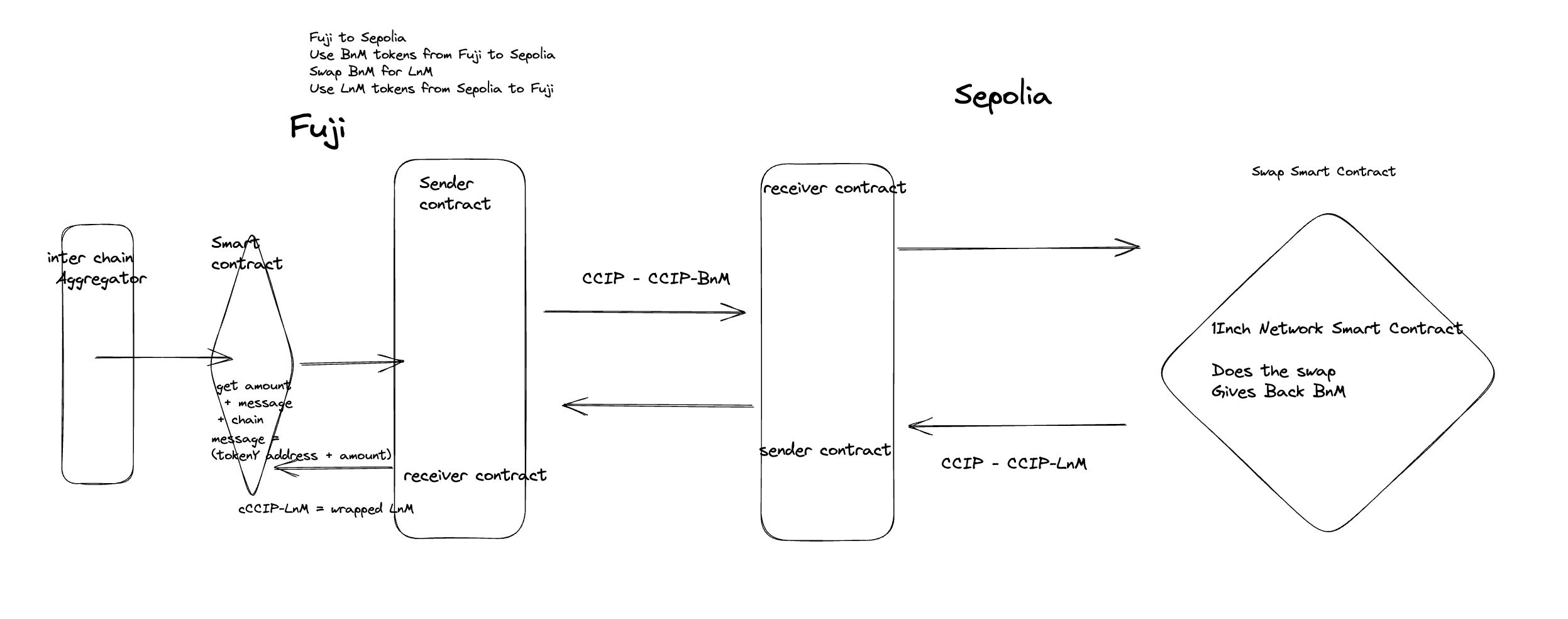
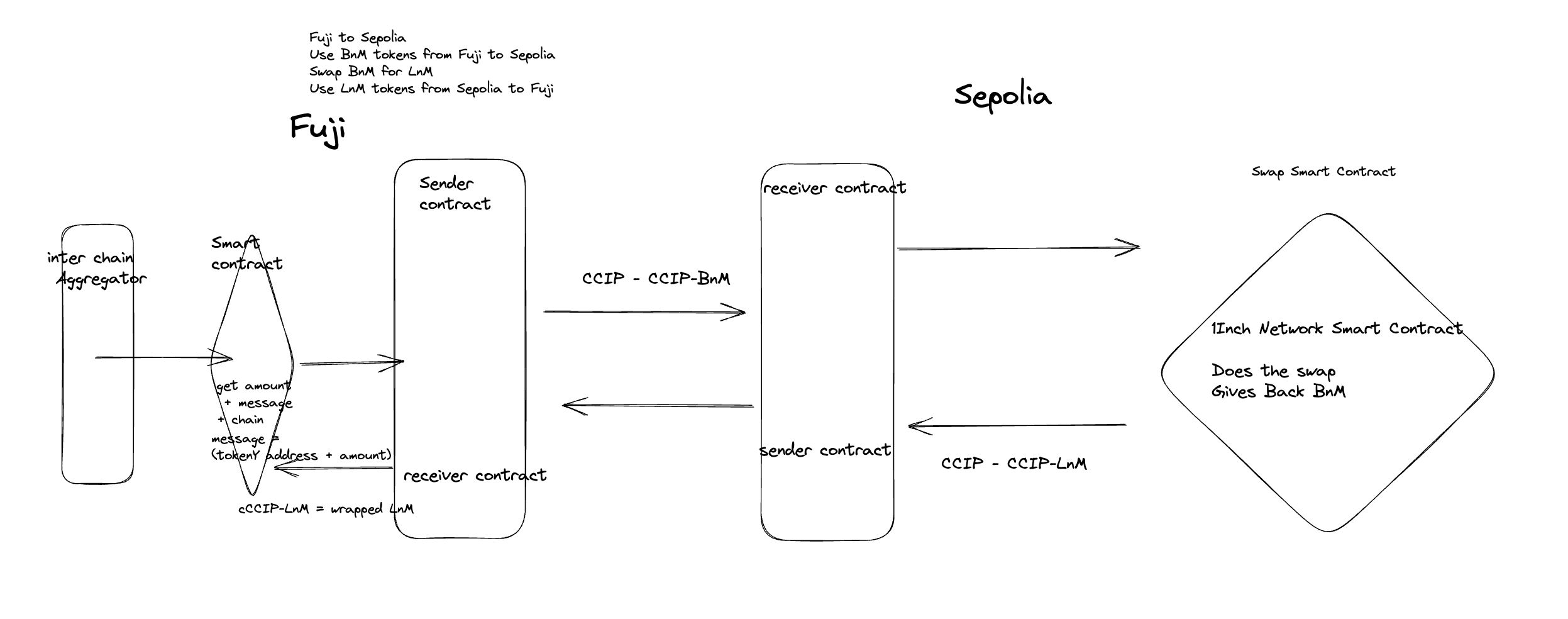
This protocol is built in three parts, with the 1Inch Aggregator on the one side, the 1inch smart contracts on the other side and the CCIP protocol on the middle.
The entry point is when a user wants to swap two coins through our Poseidon Swap protocol. We fetch the best route and the best blockchain on which the funds will get the (lowest slippage )and the lowest price impact by querying every 1Inch API on each chain and aggregating them together.
Secondly, we deploy a Programmable Token Transfer (PTT) contract on every supported chain (at least two chains) from which we will be able to “bridge” tokens back and forth. These contracts call the CCIP routers on each side of the chain. Thus on the sending chain, we have a PTT contract that call the send function of the router. On the other side, on the receiver chain PTT, we have a function that waits for a call to its receive function.
Finally, upon call of the receiver PTT listening function, this function triggers a swap that uses the 1Inch aggregator on the receiving chain. The swapped token is then sent back to the source chain using a CCTP send function call from the destination chain PTT.