Acid chains
Unlocking Ethereum's potential with the Acid chains, pushing scalability to the max, reducing transaction times, cost and fostering innovation, all within existing nodes.
Acid chains
Created At
Winner of

🥇 The Graph — Best New Subgraph

🏊 Push Protocol — Pool Prize
Project Description
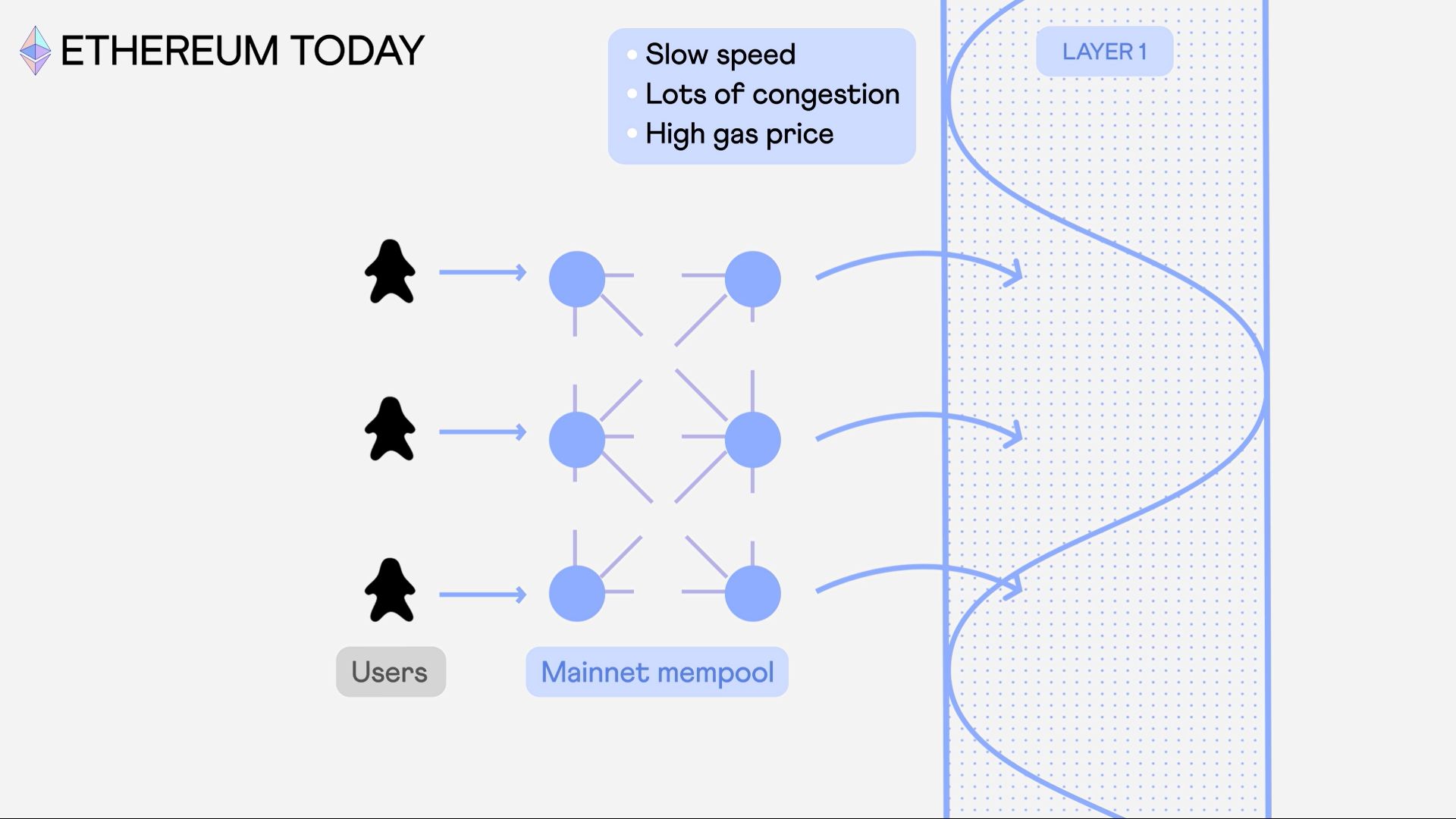
The Acid chains are a transformative project that aims to address Ethereum's scalability challenges while promoting faster, improved and more cost-effective transaction processing. At its core idea, the Acid chains involves modifying an Ethereum full node to work with an Acid Virtual Machine (AVM) and a specially optimized mempool.
In this unique setup, the mempool retains a select number of priority transactions from the Ethereum mainnet (~1,000,000), prioritizing those with the highest gas prices. Simultaneously, it holds on to a category of "special transactions" indefinitely unless they are marked as used and deleted by the AVM.
The AVM plays a pivotal role in processing and managing these special transactions. It runs on the same nodes and is designed to construct blocks using various consensus methods depending on the developer purposes, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), Proof of Work (PoW), and Proof of Authority (PoA). Once a block is built, all transactions included within it are deleted from the special transactions section of the node mempool, streamlining the process and managing mempool space effectively.
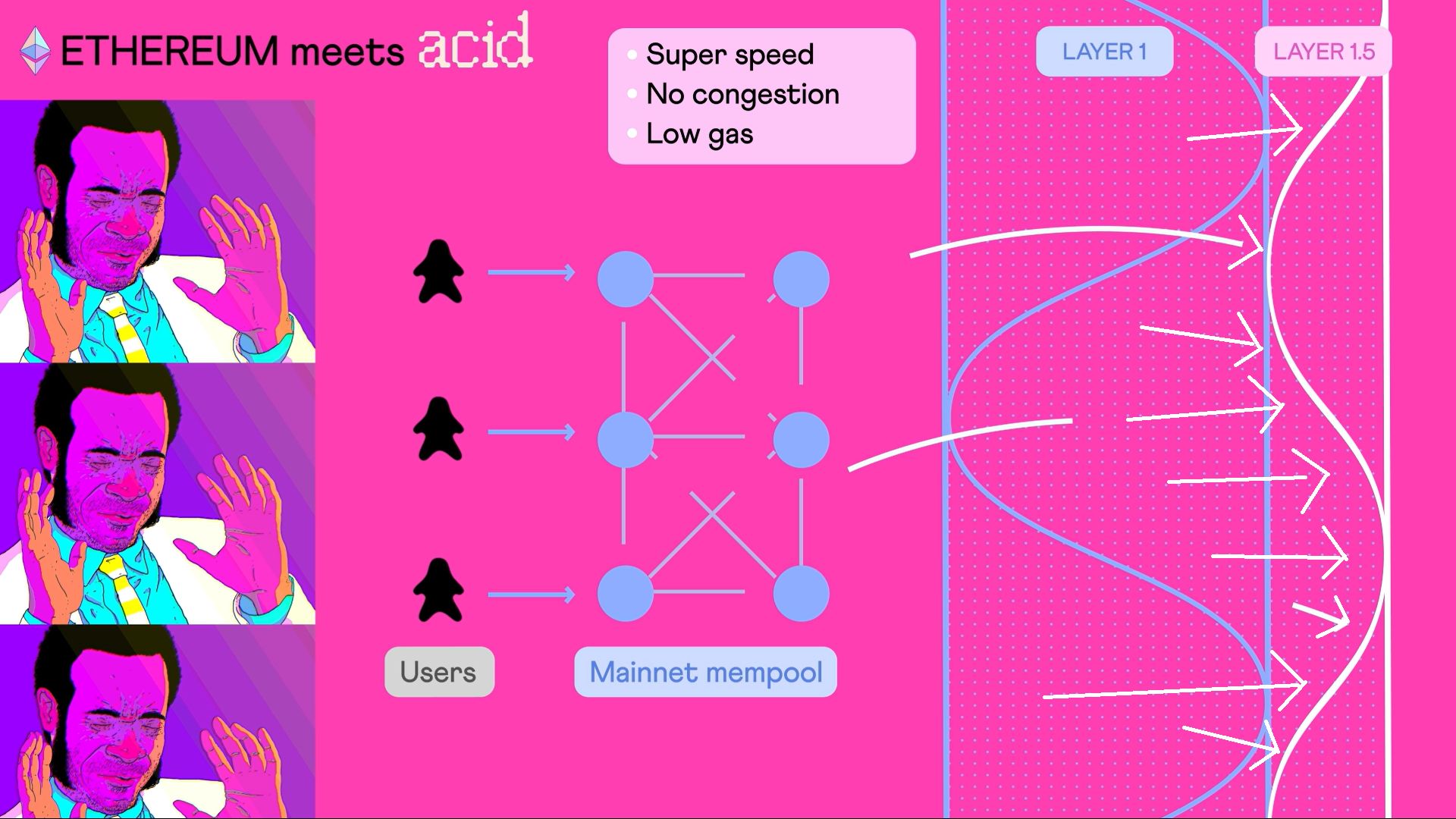
This approach to layer 1.5 blockchain creation, because we are using the same mempool than Ethereum mainnet, offers several distinct advantages. In example, by using the minimal gas fee, the ACP reduces gas costs significantly. Each confirmed transaction acts as a checkpoint for the layer 1.5 in mainnet, with special blocks created to record this information.
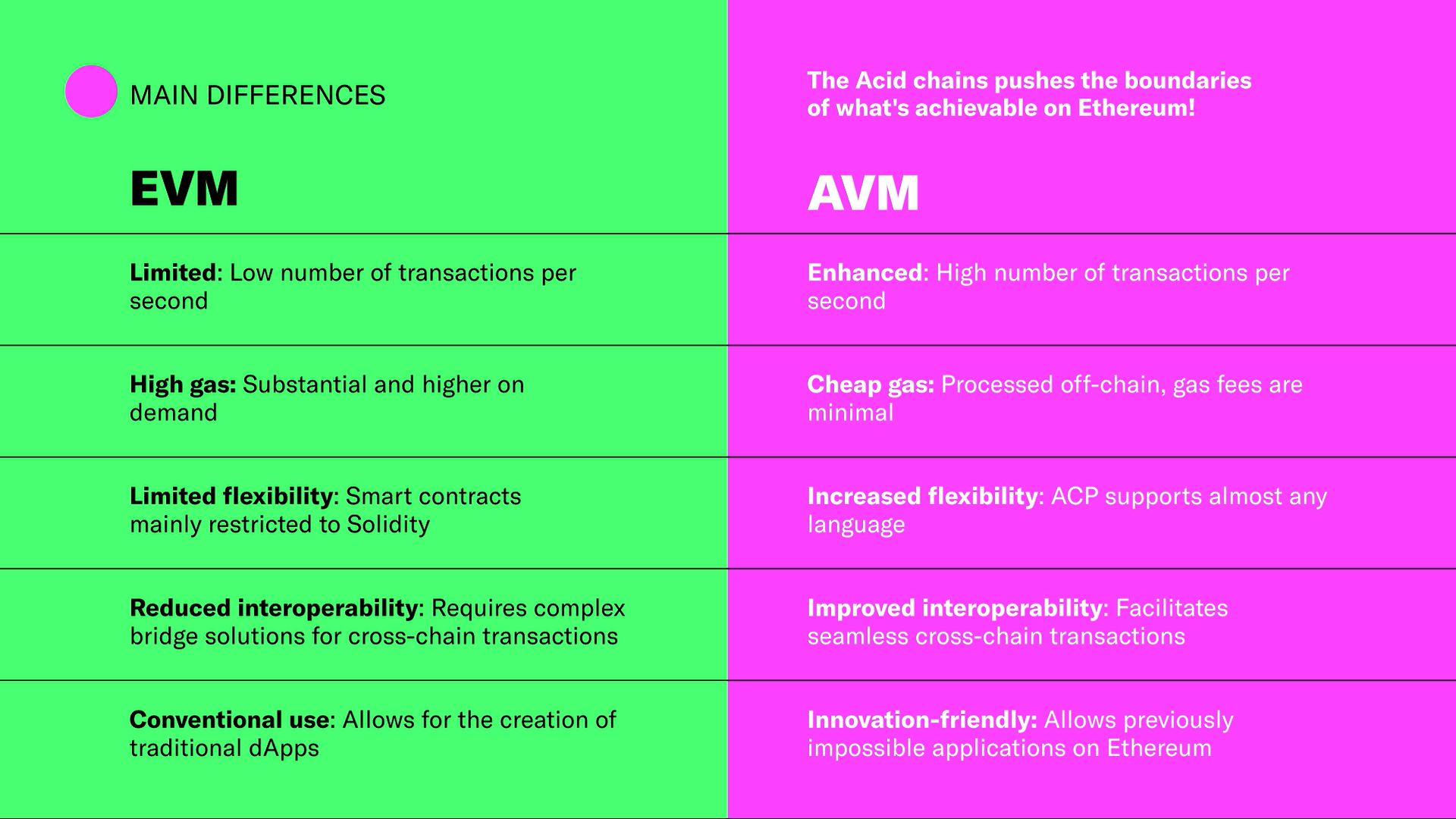
Also, the Acid chains goes a step further with its AVM capable of parsing JavaScript (at least, and for this PoC made 100% in the hackathon), which opens the door for on-chain and off-chain actions, along with the creation of innovative, complex metaprotocols for each implementation. This additional level of flexibility allows the AVM to manage malformed or false positive transactions effectively and expands the range of possible actions on the chain.
In summary, the Acid chains (L 1.5's) offers a novel way of leveraging the existing Ethereum network to increase scalability, speed up transactions, and significantly reduce costs. With the ability to support a wide range of applications from gaming, token swaps and DAOs to data sharing, DeFi, and DEX, the Acid chains are poised to push the boundaries of what's possible on Ethereum.
How it's Made
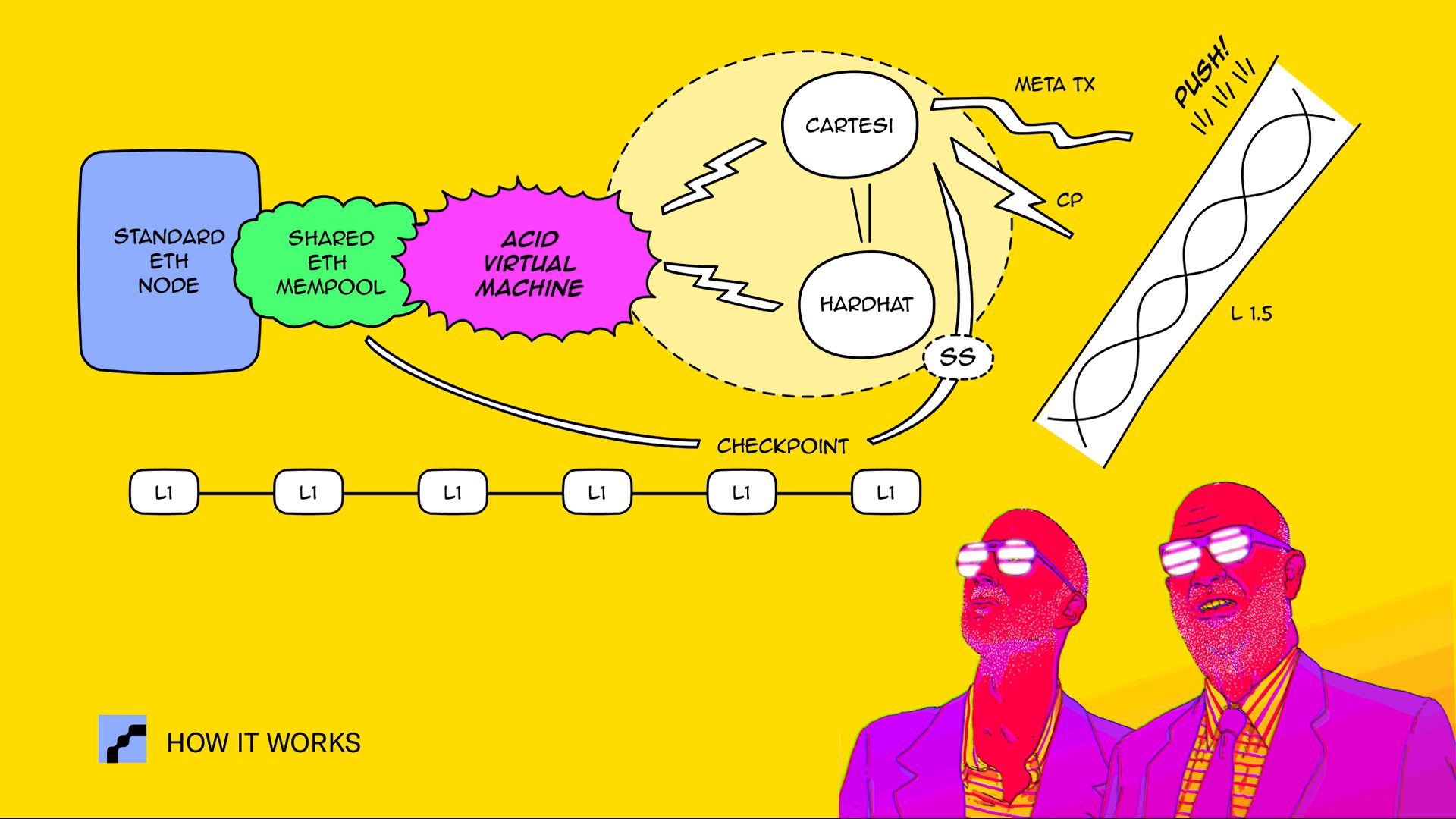
For this proof of concept (PoC), we leveraged a range of established technologies to bring the Acid Chain Protocol to life. We deployed a node using QuickNode, which served as our base infrastructure. To modify the node's mempool behavior according to our needs, we developed an add-on for the QuickNode marketplace. This was instrumental in filtering the node's mempool and feeding it into our specially constructed Acid Virtual Machine (AVM).
The AVM, a pivotal part of our setup, was designed to process the incoming transaction data, construct node attestations, and store these in a smart contract developed using the Hardhat Ethereum development environment. The smart contract is then consumed by a Cartesi Machine which writes the Layer 1.5 blockchain, emulated for this PoC, block by block.
To ensure that users are informed promptly about block confirmations, we incorporated the Push protocol. The Graph Protocol, on the other hand, was utilized to discover Checkpoints using Substreams, adding an extra layer of security and reliability to the system.
At this stage, the AVM is fairly rudimentary and solves a simple mathematical challenge, representing a straightforward use case. Our chain for the PoC was built using Proof of Authority (PoA) consensus thanks EAS attestation. However, the AVM's potential is vast, and its flexibility allows it to process virtually any kind of logic, facilitating more complex use cases in the future.
It's important to highlight that all these components, although not tested in production, are publicly available for download, deployment, and experimentation. This enables anyone to construct their experimental Acid Chains, promoting open-source development and innovation in the field. Please note that these are experimental tools and should be used with caution.
For the demo dApp we are using wallet connect.